Some emphasize that product development begins with writing code and that effort transforms into a win. The lingering question for this type of three-part development model is “What is Phase 2?”

Some emphasize that product development begins with writing code and that effort transforms into a win. The lingering question for this type of three-part development model is “What is Phase 2?”
What is Valued by Gnomes that Code?
Many managers track business metrics and project metrics during Phase 2 to forecast the potential to win.
What is valued by gnomes that code?
Gnomes associate winning with factors that include autonomy, mastery, and purpose. Dan Pink wrote about what motivates individuals in his book Drive.
Gnomes can develop autonomy, mastery, and purpose in an environment when there is a moderate amount of volatility, randomness, disorder, and stressors. Gnomes can benefit in a development environment that is characterized by a moderate amount of adventure, risk, and uncertainty. Taleb called this type of environment antifragile.
Development Options
Taleb wrote ‘The option is an agent of antifragility.’ An agent obtains results.
An appropriately designed network continuously synthesizes development options that provide the potential to take action that may result in a favorable gain. When an attractive gain may be realized, options are exercised.
Development options:
- Include tasks that are likely to improve the antifragility of the network during a project
- Are a response to the question ‘what should the network embrace now to improve the potential to win in the future?’
- Are continuously synthesized and exercised during a project within the development network to refine the focus and direction of efforts to generate a win
- Are consistent with the concept of safe-to-fail experiments that have an asymmetric payoff function (large potential gain, small potential loss)
- Are exercised, evolve, or expire
The capabilities of the network impact the attractiveness of the development options that are generated.
To the extent that options are exercised and provide feedback, confidence in their attractiveness tends to increase.
Multiple options can be active simultaneously to provide multiple opportunities to win within the network’s current capabilities and within the project’s current constraints.
Precursors to Development Options
Analysis is a precursor of synthesis. Analysis is a problem solving approach that divides the whole into its constituent parts. Synthesis is a process of connection.
A synthesis approach enables one to imagine how several capabilities may work together to produce the desired result. Validation may follow from a combination of decision, action, interaction, and more observations.
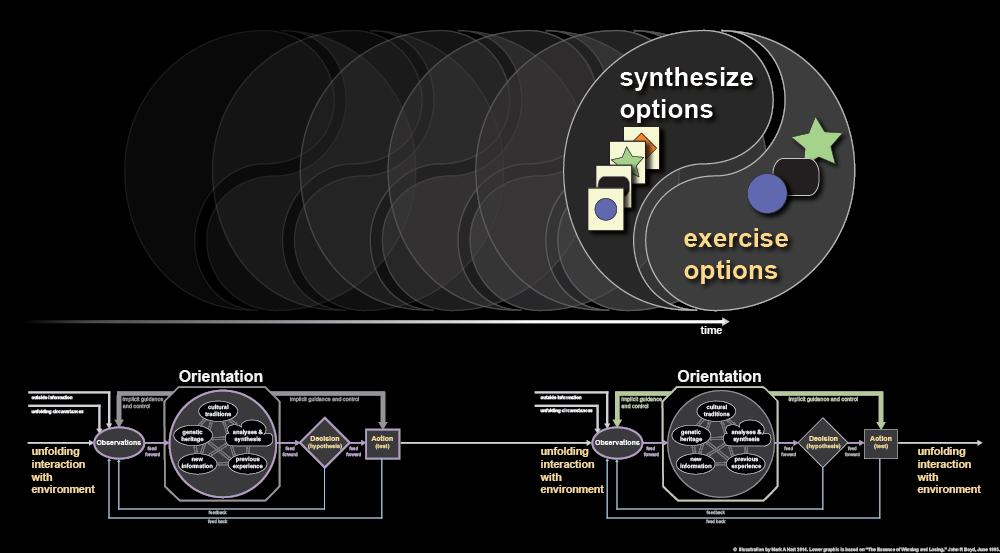
John Boyd represented these items in his OODA Loop sketch in his final briefing titled “The Essence of Winning and Losing” in 1995. I have expanded Boyd’s notation to represent the interactions of individuals and their efforts during a project.
John Boyd’s OODA Loop sketch notation can be expanded to represent the interactions of individuals and their efforts during a project. This illustration includes the representation of simultaneous efforts within a hierarchy and the pursuit of two options simultaneously.
The following notation represents synthesizing options and exercising options throughout a development project.
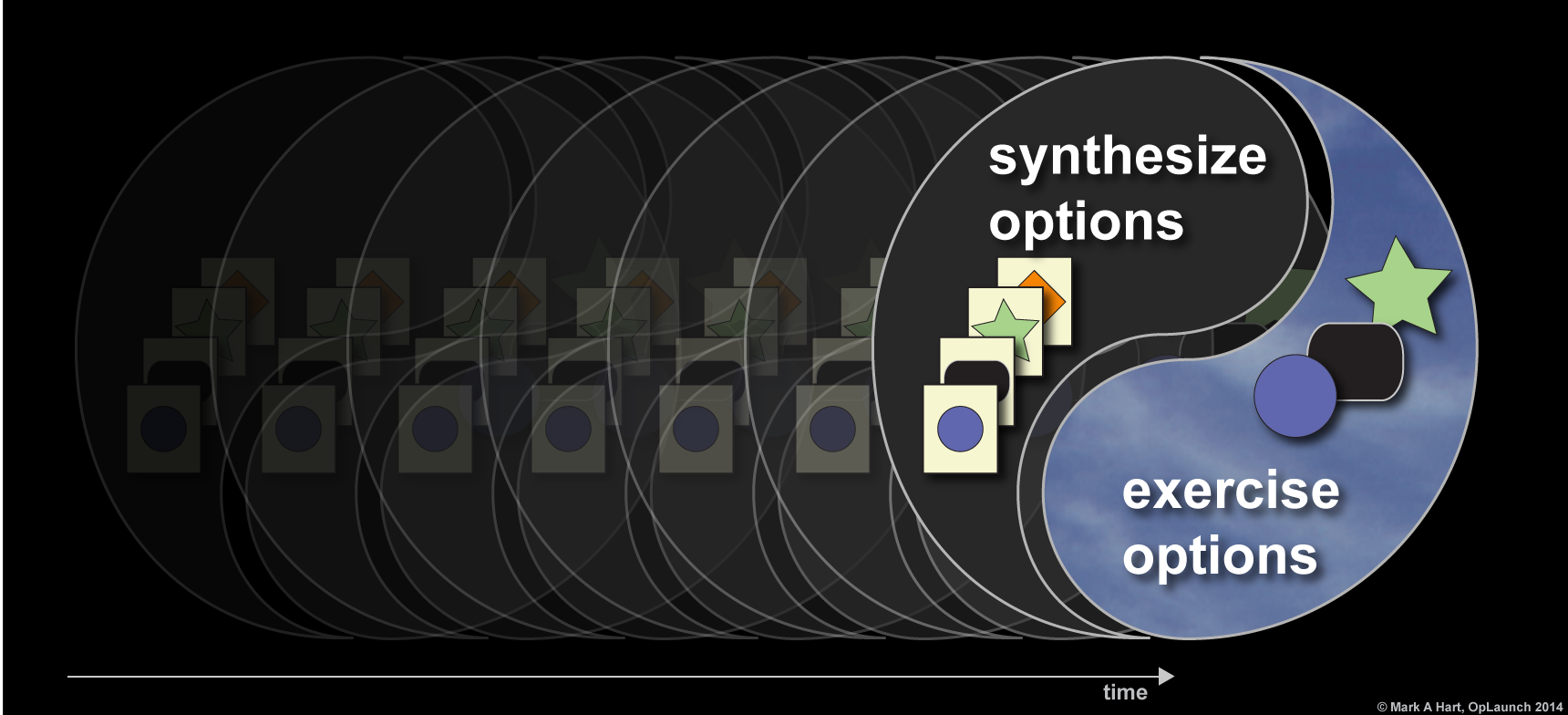
Synthesizing many options and exercising attractive development options should occur rapidly throughout a project. ‘Synthesize options’ includes imagining solutions and documenting them. The cloud filled sky background of the ‘exercise option’ portion of this graphic represents the interaction of prototypes with the environment (which includes customers).
Designing to Improve the Capability to Synthesize and Exercise Attractive Development Options
Optionality can be improved by design. Concepts that can be employed in a development environment to help gnomes that code improve their capability to synthesize and exercise attractive development options include:
- Requisite variety
- Pair Development
- Disintermediation
- Recursion
When the network has requisite variety, the network has to potential to recognize all problems and to activate appropriate responses.
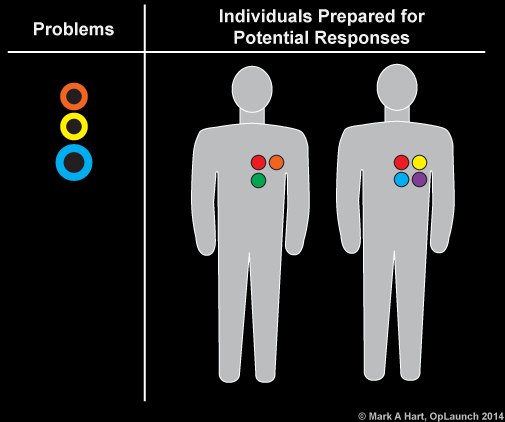
Requisite variety addresses the importance of having proficient practitioners with a diversity of capabilities that can be mobilized in a dynamic network. The table indicates that this environment has requisite variety because the number and type of responses represented are greater than or equal to the number and type of problems represented.
Requisite variety is associated with mobilizing a network of contributors with diverse specialties and multiple perspectives. To be successful, individuals may require additional training, access to individuals with unique expertise, and new ways to cooperate.
During the project, individuals engage and disengage to maintain requisite variety and avoid the paralysis associated with excessive variety.
Pair Development facilitates the synthesis of options to develop a self-correcting focus and direction informed by the analyses of multiple perspectives.
Pair development is implemented by facilitating the interaction of individuals of different disciplines (such as a coder and a market specialist). Pair development may include activities such as dialog and sketching.
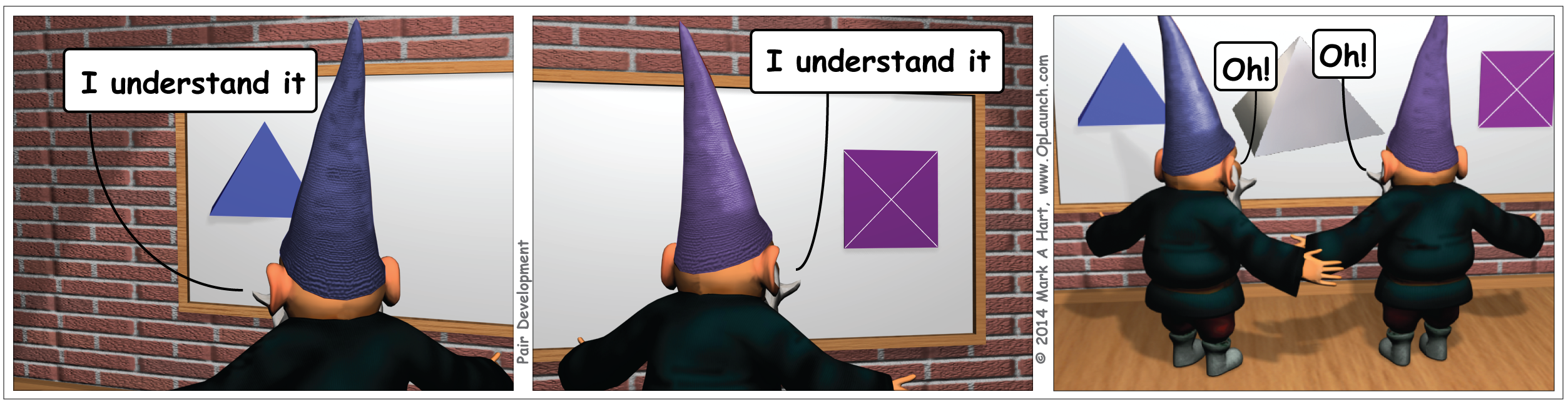
Pair development provides an opportunity for interaction through activities such as dialog and sketching to transform orientations. The result of pair development should be a synthesis of options, not a summary of previous activities.
Pair development provides benefits beyond distributed cognition. The purpose of pair development is not cross-training. The result of pair development should not be a summary of previous activities.
Disintermediation efforts may involve removing layers of management or removing other barriers. Disintermediation efforts may have objectives such as:
- Improving agility
- Rapid recognition of problems
- Rapid implementation of solutions
- Faster cycle times
Achieving these objectives may require the re-design of the network to facilitate communication, cooperation, collaboration, and harmony among individuals.
Achieving these objectives may require evolving the way that individuals experience the interactions of customers with prototypes (or other experiments related to the product being developed). Direct observations that promote full-fidelity interactions are preferable to mediation approaches such as presenting individuals with reports that summarize activities.
Recursion is a solution or technique in which large problems are solved by reducing them to smaller problems of the same form.
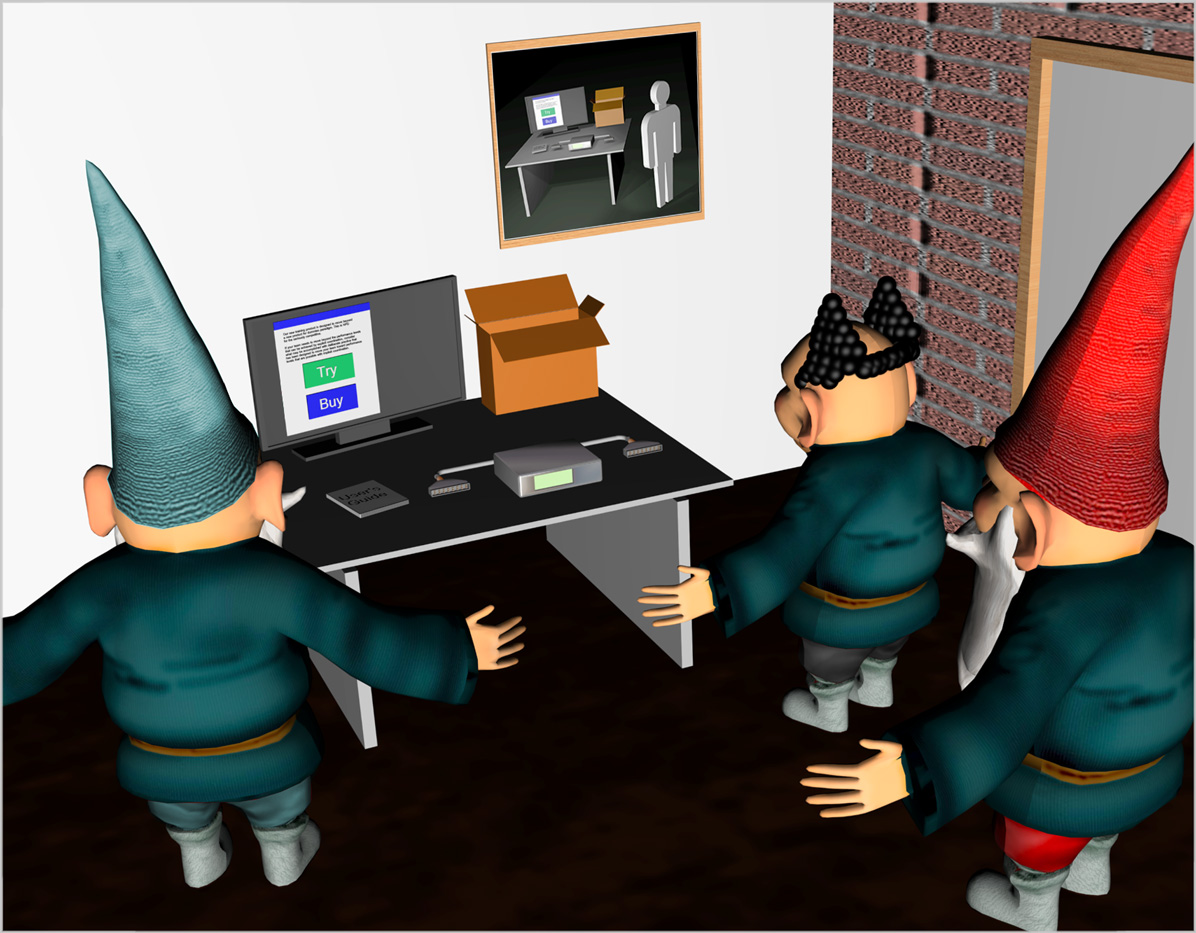

Recursion is a solution or technique in which large problems are solved by reducing them to smaller problems of the same form. A recursion approach works best in a development network with requisite variety that observes the interactions of multiple potential customers with evolving, functional, holistic prototypes.
The network’s perceptions of large problems shape the focus and direction (schwerpunkt) of the project. When developing a new product, the large problems include the customer’s experience with the product.
Large problems are evaluated by the interactions of people with products during activities such as buying, setup, use, maintenance, and troubleshooting. The large problems include the customer’s perceived value of the new product in comparison to alternatives. The large problems may be evaluated in terms of the delight produced using the product to accomplish a task.
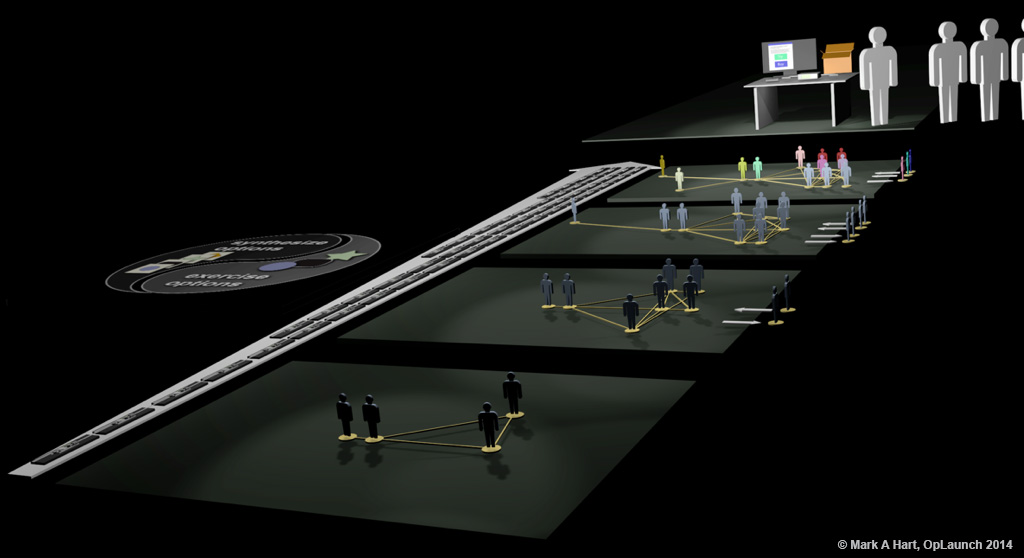
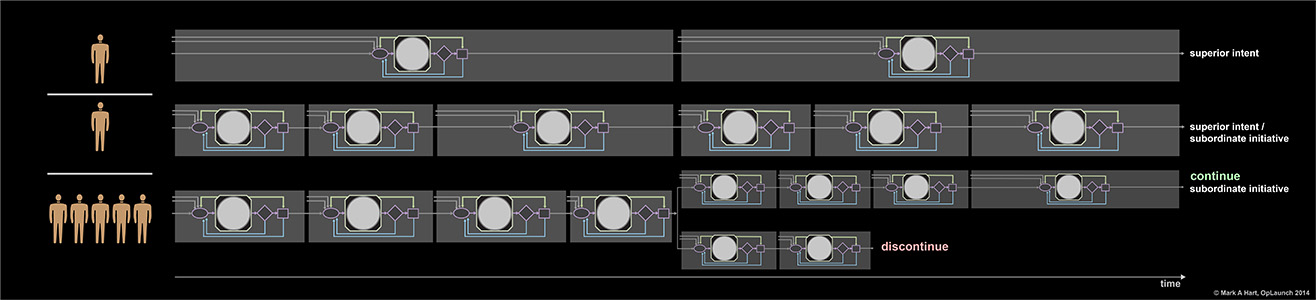
A recursion approach provides multiple channels of feedback to a development network with requisite variety that evaluates multiple opportunities to win. Customers interacting with prototypes is represented in the upper-right corner. Four snapshot of the development network are represented during the project.
A recursion approach provides multiple channels of feedback to evaluate multiple opportunities to win.
A recursion approach works best in a development network with requisite variety that observes the interactions of multiple potential customers with evolving, functional, holistic prototypes. The interactions provide multiple opportunities to detect mismatches and develop corrections.
Mismatches: the difference between the phenomena that is observed and the conceptual description of that situation
A recursion approach provides validation that is beyond the results available from surveys. Prototypes are evaluated beyond their functionality. A recursion approach includes evaluating how one user describes a solution to another user.
A recursion approach is used to validate the attractiveness of development options.
When practicing recursion approaches, individuals that tend to identify themselves as independent specialists shift to identifying themselves as contributors to development options. Their perspectives change. They engage in efforts to solve the large problems.
Transitioning from Coding to Winning
Gnomes know how to write code.
To transition from writing code to winning, gnomes benefit from concepts such as requisite variety, pair development, disintermediation, and recursion contribute to improving the capability to synthesize and exercise development options rapidly in an antifragile development environment.
This enables gnomes that code to become winners that code.
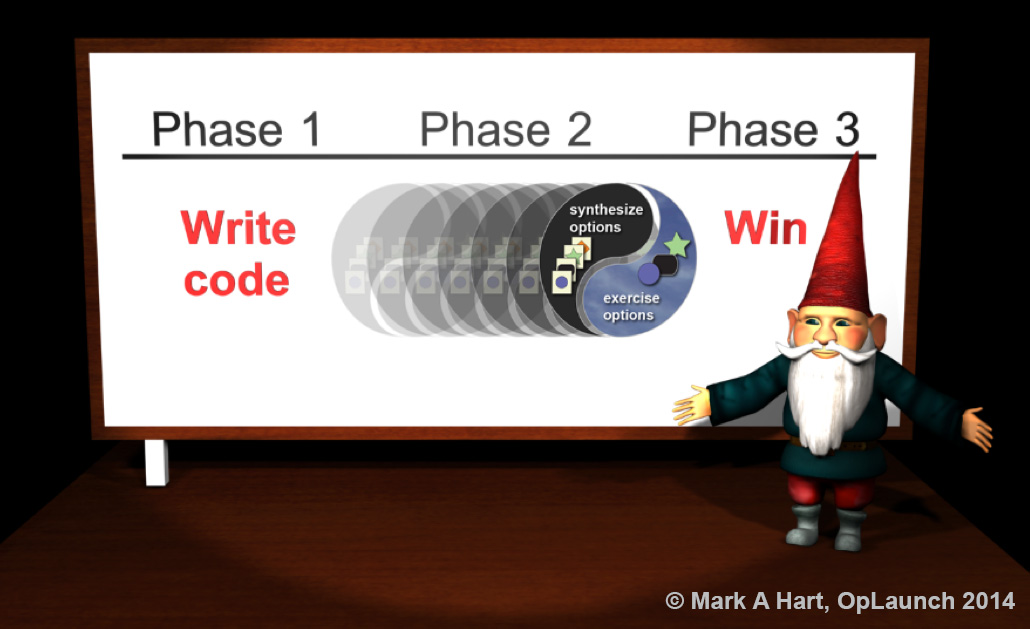
During Phase 2, the capability to synthesize many options and exercise attractive development options rapidly enables a properly prepared network of individual contributors to realize non-linear gains that are not possible by alternate development approaches such as ones that focus on managing mandates. This enables gnomes that code to transition to winners that code.
Diversity in Expressing Wins
Ultimately, gnomes that code express their wins through actions that are consistent with motivating factors such as autonomy, mastery, and purpose. Gnomes that code may express their wins to their peers through recurring actions such as pushing files to their Git repository or answering questions on StackOverflow. These types of actions improve their development experience.
When the gnomes that code win, their success propagates. Customers express their wins by actions such as posting product reviews that described how the products enable them to be successful. Managers achieve their desired business objectives and project objectives. Managers may express their wins through actions such as presentations and publication on innovation. They may be rewarded with stock options.

Individuals in different roles express their wins to their peers through unique actions. Gnomes that code may express their wins through actions such as pushing files to their Git repo or answering questions on StackOverflow. Customers may express their wins by actions such as posting product reviews that describe how products enable them to be successful. Managers may express their wins through actions such as presentations and publications on innovation.
Notes:
The “What is Phase 2?” question was included in the “Gnomes” episode of South Park, Season 2. 16 December 1998. That episode provided an inspiration for this post.
The Law of Requisite Variety was formulated by W. Ross Ashby.
This post included material from my book Developing Winners.
 [Requires iTunes or Apple Quicktime. Duration 9:24 minutes:seconds]
[Requires iTunes or Apple Quicktime. Duration 9:24 minutes:seconds]